Written by: Mr Caspar Aylott
Published: 08/04/2020
Edited by: Cameron Gibson-Watt
This article also appeared on TopDoctors
What exactly is a spinal fracture? A spinal fracture refers simply to a ‘broken bone ’in the back. We often say that someone has ‘broken their back ’when we describe someone who has a spinal fracture following a traumatic accident.
There are 33 bones in our spine known as vertebrae that provide support to our bodies, allowing us to hold ourselves up, twist and bend over. Fracturing one or more of these bones can be demobilising and requires a lot of rest and specialist treatment – other times it’s not that serious.
In this article, leading spinal surgeon, Mr Caspar Aylott, discusses the various causes of a spine fracture, how you can prevent it from happening and what the main forms of treatment are.
What is a spinal fracture?
A spinal fracture refers simply to a ‘broken bone’ in the back.
What does a spinal fracture look like?
There are many different types of spinal fracture but they all produce back pain.
Fractures may involve an important weight bearing section of the spine or part of the bone which has muscles or ligaments attached.
Some spine fractures are serious and some are not.
Serious fractures are usually caused by a high energy injury such as a road traffic accident, falling from a horse or height, extreme sports etc
Specialists assess fractures to determine if they are stable or unstable.
Unstable fractures may result in damage to the nerves or spinal cord leading to paralysis or death.
What can cause a spinal fracture?
I see four main reasons for having a spine fracture:
- Insufficiency fractures – Weak bones in elderly. No trauma.
- Traumatic fractures – Strong bones in young. Violent trauma.
- Stress fractures – Strong bones in adolescence. Repetitive minor trauma.
- Pathological fractures – Weakened bone by cancer. No trauma.
How can you prevent a spinal fracture?
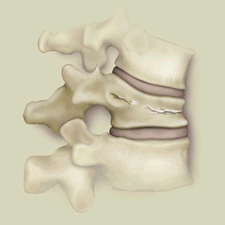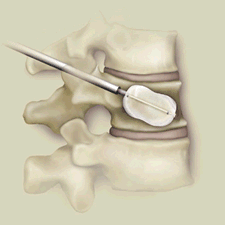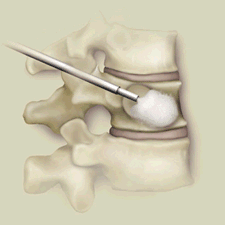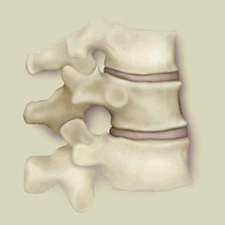
Figure 1 shows typical compression fracture in the weight bearing part of the vertebra.
Avoid accidents and extreme sports!
BUT you can’t go through life ‘wrapped in cotton wool’ and ‘accidents do happen’!
However the most common type of spinal fractures are not related to accidents but a weakness of the bones as we get older. (Figure 1)
This ‘thinning’ of the bones may be referred to as osteoporosis and is also the cause of wrist and hip fractures in the elderly.
Osteoporosis is more common in females following early menopause, but family history, long term steroids etc are important and we mustn’t forget men can also suffer.
Diagnosing osteoporosis early, before fractures happen, is really important and a good diet, regular exercise and medical treatments can really help to reduce fractures.
How to treat spinal fractures?
Treatment depends on the type of fracture.
Unstable fractures move out of place (displace) when we stand.
Most unstable spine fractures need surgery with strong metal screws and rods to hold the spine together allowing bone healing.
Sometimes a patient may be confined to flat bed rest for several months allowing the fracture to heal or ‘set’.
A neck or back brace may also be worn for three months.
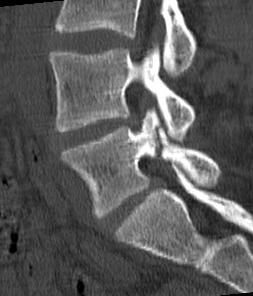
Figure 2. Can you see the stress fracture at the lower lumbar level of the spine?
Insufficiency fractures caused by osteoporosis are normally stable.
Osteoporotic bone breaks more easily but essentially heals normally and fractures heal over 3 months or longer with plenty of reclined rest.
Cement can be injected into insufficiency fractures to quickly improve pain and walking and help restore the normal shape of the bone. This is called Balloon Kyphoplasty.
Stress fractures are a very specific type of fracture usually found in the lower back. They usually produce back pain in sporty teenagers, classically dancers, cricket bowlers, gymnasts, etc Treatment usually requires several months of rest to give the fractured bone a chance to heal. (Figure 2)
Pathological fractures are usually caused by cancer (myeloma, breast, lung, prostate, kidney cancer etc) spreading into the spine and weakening the bone. Treatment usually involves drugs and/or radiotherapy (powerful X-rays) to kill the cancer. Surgery may also be necessary if the spine fracture is unstable.
Summary
It is important to remember that a simple Xray taken by the GP or through A and E does not necessarily exclude a spine fracture. More advanced imaging may be necessary.
We can investigate your back pain properly and without delay and provide you with both an accurate diagnosis and the correct advice and treatment.
For enquiries and appointments please call:
Victoria Clarke – Practice Manager
01242 371281
victoria@cheltenhamspineclinic.co.uk

